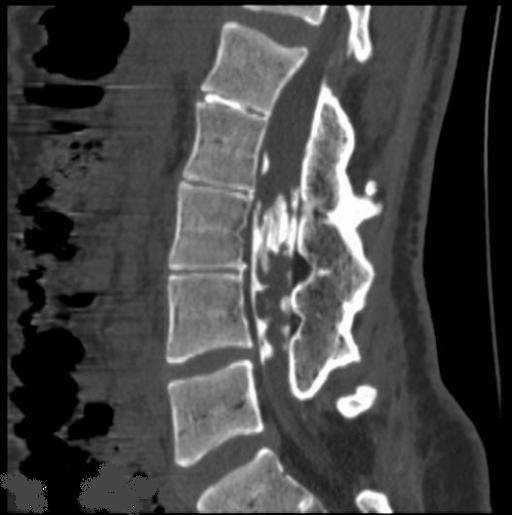
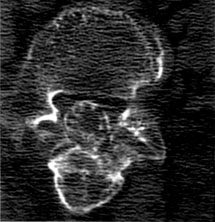
Arachnoiditis ossificans
Arachnoiditis ossificans is a rare type of arachnoiditis, with about 46 cases reported in the world literature today. It has received little attention in the neurosurgical literature. Spinal arachnoiditis ossificans can present with a wide variety of signs and symptoms, depending on the location, morphology, and size of the lesion.
Predisposing factors for the development of the disease are similar to those for adhesive arachnoiditis and include trauma, hemorrhage, and meningeal irritation. Unlike adhesive arachnoiditis, arachnoiditis ossificans has been treated successfully with surgery. Surgery, however, remains a controversial treatment option.
Consequently, the literature and available case reports on arachnoiditis ossificans were reviewed to gain a better understanding of the disease, its presentation, etiology, treatment options, and prognosis. The disease is optimally evaluated by noncontrast computed tomography. Treatment decisions are based on the location and morphology of the calcifications and their contribution to compression of the spinal cord or nerve roots. Most patients with arachnoiditis ossificans do undergo surgery and most improve.